- Allow Traceroute Through Windows Firewall
- Allow Traceroute Through Checkpoint Firewall
- Enable Traceroute Through Firewall
Ping and traceroute are tools used by engineers to troubleshoot network connectivity. In order to permit an outbound ping permit ICMP echo-request, to allow a reply through a firewall the ACL on the OUTSIDE interface must specifically permit an echo-reply inbound.
Traceroute usually uses UDP probes and ICMP replies, the client computer sends 3 x UDP probes (in the range 33434 – 33464) per hop, except Windows Operating Systems which uses ICMP echo-request probes. To permit ICMP and traceroute outbound permit ICMP and UDP (33434 – 33464), to permit traceroute replies ICMP Type 3 (destination unreachable) and 11 (time exceeded) must also be permitted from OUTSIDE to INSIDE.
This blogpost describes how to permit outbound ICMP/Traceroute and the inbound replies on a Cisco Firepower Threat Defense (FTD) Firewall.
Configure ICMP/Traceroute
Hi Frank, Basically when a traceroute is issued on a Cisco device it would initiate traffic sourcing from a random port to the destination port UDP/33434 (UDP port 33434 is the first one used by traceroute as the destination port) and it will increment that destination port number until the datagram is. I was under impression that allowing icmp in the service policy will enable tracert to work. After scouting around I found below tweaks that will enable tracert to run correctly. It looks like your connection is getting lost when it goes through the IP 78.40.148.10, You should contact your ISP and provide them your traceroute so they can correct that issue if that route belongs to them or work with whoever it belongs to to resolve the issue. The client decides it has sent too many sets of traceroute packets (the default is 30) and stops. For any firewall solution to securely allow traceroute through, 2 it must take all of these situations into account. Let's explore how each of the firewall technologies can address passing traceroute. Hello, I have a checkpoint ng r55. I allow a icmp (all types) connection: The host 10.1.1.1 can ping 20.2.2.2. When host 10.1.1.1 traces the route to 20.2.2.2, it get a pesponse from the firewall internal and external interface!
Define an object for UDP Probe ports
- Navigate to Objects > Port
- Click Add Port
- Define an appropriate name e.g. UDP_Traceroute
- Select UDP
- Define port as 33434-33464
- Click Save
Configure Oubound ACP rule for ICMP/UDP Probes
- Navigate to Policies > Access Control > Access Control
- Click on existing policy
- Create a new rule called ICMP Outbound
- Click Zones and select the Source Zone as the INSIDE zone(s) and select the OUTSIDE zone as the Destination Zone.
- Click Ports and add ICMP (1) and UDP_Traceroute to Destination Ports
- Click Save
Configure Inbound ACP rule for traceroute and ICMP replies
- Create a rule for ICMP/Traceroute replies, called ICMP Inbound
- Click Zones and select the Source Zone as the OUTSIDE zone and select the INSIDE zone(s) as the Destination Zone.
- Click Ports and add ICMP (3), ICMP (1) 11 and ICMP (1) 0 to Destination Ports
- Click Save
- Click Save to save the changes to the ACP
- Deploy the policy
Traceroute from a computer should reveal all the IP addresses of each hop towards the destination.
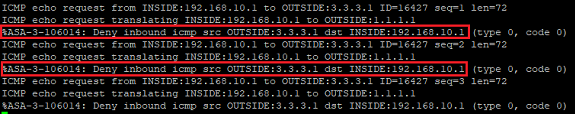
In this example 192.168.10.1 is the SVI of the local switch, the IP address of the firewall is 192.168.100.1 which does not appear as a hop in the traceroute. Hop 2 is the ISP router, which is possibly filtering responses which is why the request times out.
Enable FTD to appear as a hop in traceroute
The FTD firewall does not appear as a hop when performing a traceroute from inside the network to outside. This is because by default the FTD does not decrement the Time To Live (TTL) on packets that pass through the device. Previously on the FTD you had to configure a FlexConfig policy in order to decrement the TTL, since the latest versions of FTD you now use a “Threat Defense Service Policy”.
Create Extended Access List
- Navigate to Objects > Object Management > Access List > Extended
- Click Add Extended Access List
- Click Add to add a new sequence
- Select Action to Block
- Click Port tab
- Add OSPFIGP (89) to destination port
- Click Save
- Click Add to add a new sequence
- Click Add
- Click Save
Allow Traceroute Through Windows Firewall
Modify the Access Policy Service Rule
- Navigate to Policies > Access Control > Access Control
- Modify the existing ACP
- Click the Advanced tab
- Click the edit button next to the Threat Defense Service Policy
- Click Add Rule
- Click Next to leave as the Global interface object
- From the Extended Access List drop-down list select the ACL previously created called traceroute
- Click the Enable Decrement TTL option
- Click Finish
- Click Ok
- Click Save to save the updates to the ACP
- Deploy the policy
Traceroute from a computer should reveal all the IP addresses of each hop towards the destination, now including the IP address of the FTD (192.168.100.1) as the 2nd hop.
Home > Articles > Security > Network Security
Allow Traceroute Through Checkpoint Firewall
␡- An Overview of Firewall Security Technologies
This chapter is from the book
This chapter is from the book
An Overview of Firewall Security Technologies
Many companies engage in marketing hype to try to prove that their technology is better. Despite the hype, all firewall security technology can be broken down into three basic types: packet filtering (stateful or otherwise), application layer gateways, and Stateful Inspection.
Packet Filters
Packet filters screen all network traffic at the network and transport layer of the TCP/IP packet. This means they look at source and destination IP addresses, protocol number, and, in the case of TCP and UDP, source and destination port numbers. Packet filtering is built into routers as well as some UNIX kernels. Usually, when site administrators start thinking about network security, they start with packet filtering because it is inexpensive. Most routers on the market today, even consumer-grade models, support some form of packet filtering. Because routers are needed to connect different networks together (especially when connecting to the Internet), the additional cost for using this technology is minimal. Packet filtering requires very little extra memory and processing power, so even a low-end router can handle a fairly moderate load. Packet filtering is also fairly transparent to legitimate users.
Traditional packet filtering is static, that is, the only criteria for allowing packets are whether or not the IP addresses or port numbers match those specified in the packet filter configuration. Many packet filters today implement some concept of the 'state' of a connection, using a table and additional information in the TCP headers to track previously allowed packets within a connection. This makes it much easier to allow only, for instance, outbound connections from a trusted network to an untrusted network without inadvertently allowing unrelated packets from the untrusted network to the trusted network.
The biggest downside to packet filters is that they are difficult to maintain. Although this point is certainly arguable, even an expert can have trouble configuring a moderately complex set of access lists or Linux ipchains rules. Many consumer-grade routers that have packet filtering do not have an adequate interface or are very limited in what they can filter.
Packet filters also do not screen above the network and transport layers. This means they cannot do things like:
Provide content security (e.g., virus scanning or filtering based on specific sites and Web pages accessed)
Authenticate services (i.e., make sure only authorized users use a service)
Dynamically open and close ports for applications as they require them (necessary for applications like RealAudio, FTP, and H.323 applications)
Validate a particular port that is used only for a specific service (e.g., making sure that only valid HTTP traffic traverses port 80)
Application Layer Gateways
Application layer gateways, also known as proxies or application proxies, take requests from clients and make them connect to servers on the client's behalf. In some cases, the client explicitly connects to the proxy server. In other cases, the proxy intercepts the connection with help from the underlying operating system or network architecture. Because an application proxy is usually specific to the network service, it can be fully aware of the session. This means the proxy can do content screening, provide authentication, and ensure that only the particular service is used (e.g., an HTTP proxy can make sure that only HTTP traffic is allowed through), or it can provide other application-specific services such as caching. It also provides a well-formed connection to servers on the other side of the firewall because it opens up connections on behalf of the clients.
However, this extra capability comes at a price. Application proxies require memory and CPU cycles just like any other application. Generally speaking, application proxies use more memory and CPU cycles than packet filtering, although how much they use depends on the specific circumstances. If you want to use application proxies to provide services to the Internet, each application you want to run through your firewall must have a proxy written for it, or the application must be compatible with a 'generic' proxy that will work with simple TCP or UDP connections. Because many applications are not being developed to work with an application proxy, some applications simply cannot be proxied. The client/server model is somewhat broken by application proxies because the application proxy will always originate the connection from the server's point of view.1 In large environments, the poor throughput of application proxies is another drawback.
Another important drawback of a proxy, particularly for internal use, is that it becomes very difficult to track who is going where for how long because the proxy often masks the original source or destination of the traffic. You might be able to track this on the firewall, but from any other vantage point on the network, how do you know?
Stateful Inspection
Stateful Inspection combines the best features of stateful packet filtering and application layer gateways. Check Point's Stateful Inspection engine rests be tween the data link and network layers (e.g., between the network interface card and the TCP/IP driver). TCP/IP packets from the network layer and higher are scanned according to your security policy and will be either allowed through or stopped. The TCP/IP stack will not see dropped or rejected packets, which can provide an extra layer of protection. Stateful Inspection can look at the entire packet and make security policy decisions based on the contents and the context of the packet, using a state table to store connection state and using knowledge of how specific protocols are supposed to operate. In the case of FTP, FireWall-1 can dynamically open ports between two hosts so that the communication will succeed and then close the ports when the connection is done. Stateful Inspection is what gives FireWall-1 'Application Intelligence' (e.g., NG with Application Intelligence, or NG AI).

Stateful Inspection requires slightly more memory and CPU cycles than packet filtering because it has to do more, but it takes substantially less memory and CPU usage than does an application proxy. Stateful Inspection is best when the engine is made aware of how a protocol functions, although Check Point does not make use of Stateful Inspection for every protocol. Because Stateful Inspection does track connection state regardless of the service, it is better than a packet filter, but you are limited to opening specific ports and allowing the traffic through without further checking.
Technology Comparison: Passive FTP
It is useful to compare how the different technologies handle complex connection types. One such connection type is Passive FTP, which is used by Web browsers when they initiate an FTP connection. Passive FTP requires:
A TCP connection from a client to port 21 on the FTP server.
A TCP connection from a client to some random high port on the FTP server for data communication. The ports used for this communication are communicated to the client when it requests passive mode via the PASV command.
For this comparison, assume that the FTP server is behind your firewall and that you need to allow people on the Internet to FTP to this machine.
Packet Filters
Enable Traceroute Through Firewall
Packet filtering can handle standard FTP quite nicely because it uses fixed TCP ports (20 and 21). However, in order to allow Passive FTP, the packet filter has to open all TCP ports above 1024 to allow Passive FTP to work with the FTP server. This is a gaping hole that can be used by programs other than FTP to compromise your systems.
Application Proxies
An application proxy is aware of the FTP connection and opens all the necessary ports and connections to complete the FTP connection. However, each TCP or UDP connection through an application proxy requires twice the normal number of connections on the proxy server (one for each side of the connection). A normal Passive FTP connection requires two open connections on a client machine. On the application layer gateway, this translates to four open TCP connections.
Most operating systems have a limit to the number of simultaneous connections they can handle. If enough connections are going through the machine at the same time, this limit will be reached, and no further connections will be allowed through. In high-performance, high-capacity networks, using a proxy for FTP connections is simply asking for trouble.
Stateful Inspection
Stateful Inspection understands connection context. When the PASV command is sent from the client to the server, Stateful Inspection reads the server's response and opens the ports necessary to complete the connection. It also restricts the IP addresses that can use these ports to the client and server. The connection then goes through the firewall normally. Because Stateful Inspection allows the native operating system to route, no connections are established on the firewall itself. Once the connection is terminated, the ports opened by the PASV command are closed.
Technology Comparison: Traceroute
Traceroute is used to show the particular path a connection will take through the various routers and gateways within the network and gives you a basic idea of the latency between any two hosts on a network. It is a common troubleshooting tool used by network administrators. There are two varieties of traceroute: UDP and ICMP. UDP traceroute is used by almost every UNIX implementation. ICMP traceroute is typically used by Microsoft operating systems, though some UNIX implementations also allow you to perform an ICMP traceroute. How traceroute functions can be used to show the strengths of Stateful Inspection and the weaknesses of packet filters and application proxies.
UDP traceroute involves sending out packets to high-numbered ports above 31000—the actual ports used will vary based on the implementation. ICMP traceroute uses ICMP Echo Requests instead. In both cases, the client generates a number of packets (usually three) over a period of time (usually one second) to the server using a time to live (TTL) value of 1. Each subsequent set of packets will have an increasingly higher TTL value, which allows the packets to get closer and closer to the server.
During a traceroute session, any of the following can occur.
The server responds with an ICMP Echo Reply message or an ICMP Port Unreachable packet (i.e., the traceroute has finally reached the server).
An intermediate router or gateway gets a packet with a TTL value of 1; it decrements the TTL to 0. Because a router or gateway cannot route a packet with a TTL of 0, it sends back an ICMP Time Exceeded message.
An intermediate router or gateway determines it has no route to the server and sends back an ICMP Destination Unreachable message.
An intermediate router or gateway fails to respond either because it is configured to not respond to or pass traceroute traffic or because it is down.
The client decides it has sent too many sets of traceroute packets (the default is 30) and stops.
For any firewall solution to securely allow traceroute through,2 it must take all of these situations into account. Let's explore how each of the firewall technologies can address passing traceroute.
Packet Filters
With packet filtering, you would have to allow the following types of traffic to pass through your packet filter:
All UDP ports above 31000
ICMP Echo Request
Conversely, you would also have to allow the following types of packets to enter your network from any host:
ICMP Echo Reply
ICMP Time Exceeded
ICMP Destination Unreachable
ICMP Port Unreachable
Although these rules would allow legitimate traceroute traffic, they can also allow network access by packets that were not in response to a valid traceroute request. In the past, these kinds of unsolicited packets were used in denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. It is important that you allow in only those packets that are in response to a traceroute or ping query. Packet filtering alone is not an adequate tool to allow traceroute to function yet protect you from possible DoS attacks. It is important to note that the UDP ports allowed could also be used for something other than traceroute.
Application Proxies
UDP can be proxied to some degree, but due to its nature, ICMP cannot be proxied, though some versions of SOCKS can proxy ICMP using special SOCKS-aware ICMP programs. In a relatively small, controlled, homogeneous environment, this may be feasible. In a large, heterogeneous environment protected by application proxies, it may not be possible to allow all clients to trace route through the firewall.
Stateful Inspection
With Stateful Inspection, you can watch for either a UDP packet with a low TTL value or an ICMP Echo Request packet coming from a particular client. Once this happens, you can temporarily permit the necessary ICMP packets to return to the client initiating the outgoing traceroute request. After you have received the appropriate response (i.e., an ICMP Echo Reply, Port Unreachable, or Destination Unreachable message) and/or after a specific period of time (e.g., 60 seconds), you can stop allowing the necessary ICMP packets to the client.
FireWall-1 statefully inspects ICMP.
Related Resources
- Book $19.99
- eBook (Watermarked) $44.79
- Premium Edition eBook $55.99
